Part 1: Cascaded Op Amp
Today we discuss about cascaded op amp circuit, which means we make a circuit with more than one op amp.
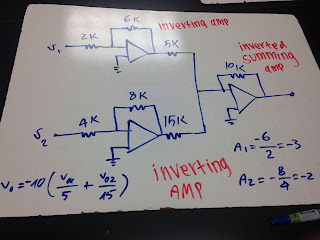
A cascaded op amp circuit including the inverting summing op amp with two other inverting op amp.
A cascaded circuit includes two non-inverting op amps. We apply the formula of the non-inverting op amp for each op amp. v(out) = (Rf+Rs)/Rs * v(in) (deduce from nodal analysis or voltage divider). To find the current i(10k)=[v(out2) - v(out1)] / 10k.
Digital - Analog Circuit.
The digital-to-analog converter DAC transforms digital signal into analog form. The bits are weights according to the magnitude of their place value, be descending value of Rf/Rn so that each lesser bit has half the weight of the next higher.
Instrumentation amplifier.
It is used for precision measurement and process control. Typical application of IA includes isolation amplifier, thermocouple amplifiers, and data acquisition systems. Function is an extension of the difference amplifier in that it amplifies the difference between its input signals.
the formula of the instrumentation amplifier. It show the different input voltages is amplified by the constant gain. If all resistances are equal except R4, called Rg, then the gain A equal 1 + 2R/Rg.
Purpose:
We apply the theory of the Wheatstone Bride Circuit and the Difference amplifier to operate this experiment and set-up the temperature measurement System Design. The requirements are,
1. The out voltage from the system is balance 0 +/- 20mV at room temperature,
2. Output voltage is positive for temperature above the room temperature,
3. he output voltage increase by a minimum of 2V over a temperature range of 25 degree Celsius - 37 degree Celsius.
Pre-lab:
1. Wheatstone Bridge Circuits: most often used to convert variations in resistance to variations in voltage. This is applied for some common sensors providing a resistance variation in response to some external influence, some of those we have discussed: thermistors(temperature), strain gages(deformation), photoconductive transducers(light intensity).
From voltage division analysis of va and vb, we have: v(ab)=va-vb= - [delta(R)/(4R)]*Vs-> v(ba)=[delta(R)/(4R)]*Vs
3. The thermistor changes as the temperature changes, Ro+delta(R), with Ro is the initial temperature at room temperature.
So, the expected process is that the change in temperature of thermistor lead to the change in resistance, then change of v(ab), the change in vo which we want to increase a minimum of 2 V
Set-up and resutls:
We set up the experiment as the video below, the videos show that the requirement results are satisfied:
Conclusion:
To analyze a cascaded op amp circuit, we either use the nodal technique to analyze this circuit or use the formulas for each kind of op amp set-up including
1. inverting op amp: vo=(-Rf/Rs)*vi
2. non-inverting op amp: vo= (1+Rf/Rs)*vi
3. summing amplifier: vo = Rf( v1/R1 + v2/R2 + v3/R3 +....)
4. difference amplifier: vo= Rf/Rs *[vi(noninverting) - vi(inverting)], if R1/R2 = R3/R4.
We did some practical problems of a cascaded circuit. We also discuss about Wheatstone and how to balance the bridge circuit. We did the lab on the temperature Measurement System Design, which combine the theory of the Wheatston Bridge Circuit and the Different amplifier. We get the expected result that qualify the requirements: the out voltage from the system is balance 0 +/- 20mV at room temperature, output voltage is positive for temperature above the room temperature, and the output voltage increase by a minimum of 2V over a temperature range of 25 degree Celsius - 37 degree Celsius.










Convertio
ReplyDeleteCloudConvert
iLoveIMG
StableAI
PDF to JPG
Land Registry Fee Calculator