Part 1: Capacitors and Inductors
We discussed about the capacitor and inductor. The professor introduced the properties of the capacitor and inuctors including current, voltage, power, and energy.
The capacitor can storage the energy and release it to the circuit. The capacitor resists to the simultaneous change in voltage.
The current of the voltage is i=C*dv/dt. So v=1/C*integral(i.dt). From the graph i vs. t, we can deduce the v vs. t
We did a practice problem on a circuit including two capacitors. We found the voltage and the energy in each capacitor.
Part 2: Capacitor Voltage-current Relations Lab
Purpose:
We will measure the relationship between the voltage difference across a capacitor and the current pass through it. We will apply several types of time-varying signals to a series combination of a resistor and a capacitor.
Pre-lab:
We deduced the graph of i vs. t from the graph v vs. t of a capacitor. i=C.dv/dt. The resistor and the capacitor are in series, so the current through the capacitor is the same as the current through he resistor. ic(t)=Vr(t)/R.
The set-up for this experiment include a capacitor and a resistor in series.
The sketches of the capacitor voltage and current for both sinusoidal and triangular input
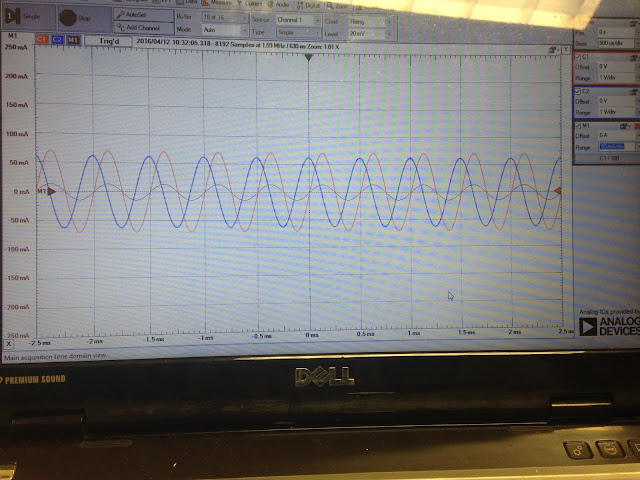
The capacitor voltage and current waveform and the measured amplitude of the waveform for a 1kHz sinusoidal input. We observed the phase shift of voltage across a capacitor. The voltage across the capacitor lags the voltage across the resistor pi/2. phil(Vc)=phil(Vr)-pi/2.
The capacitor voltage and current waveform and the measured amplitude of the waveform for a 2kHz sinusoidal input.
The capacitor voltage and current waveform and the measured amplitude of the waveform for a 100Hz triangular input.
Here the picture of a capacitor after explosion. The professor did a experiment on a polarized capacitor. If we connect a polarized capacitor improperly, it will explode.
We deduced the inductor from the capacitor properties. And The professor gave the quick and brief summary of the capacitor and inductor on the table.
In conclusion:
We examined the properties of the capacitor and inductor. We also did a experiment to observe the current and the voltage across a capacitor in a RC circuit. We found that the voltage across the capacitor lags the voltage across the resistor pi/2. phil(Vc)=phil(Vr)-pi/2.










No comments:
Post a Comment